Food handling plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of individuals. Whether it’s preparing meals at home, working in a restaurant, or handling food in any other setting, it is vital to prioritize food safety. A key aspect of this is proper handwashing, which significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses. In this blog, we will delve into the importance of maintaining food safety standards, with a specific focus on H2Safe food handling techniques and the central role of handwashing.
Understanding Foodborne Illnesses:
Foodborne illnesses are illnesses caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. The consequences of such illnesses can range from mild discomfort to severe health complications and, in some cases, even death. Common pathogens and contaminants that can lead to foodborne illnesses include bacteria (such as Salmonella and E. coli), viruses (such as Norovirus), parasites, and toxins. It is crucial to recognize the potential risks and take preventive measures to ensure food safety.
The Science Behind Handwashing:
Handwashing is a simple yet highly effective practice that helps prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and viruses. When we wash our hands, we disrupt the microorganisms present on our skin and rinse them away. Warm water, soap, and proper handwashing techniques are key elements in this process. Warm water helps to open up pores and remove dirt and oils, while soap acts as a surfactant that aids in the removal of microorganisms. Proper handwashing techniques involve thoroughly cleaning all areas of the hands, including the front and back, between fingers, and under nails. To ensure effectiveness, it is recommended to wash hands for at least 20 seconds. Lastly, drying hands with a clean towel or air dryer helps to remove any remaining moisture, which can harbor bacteria.
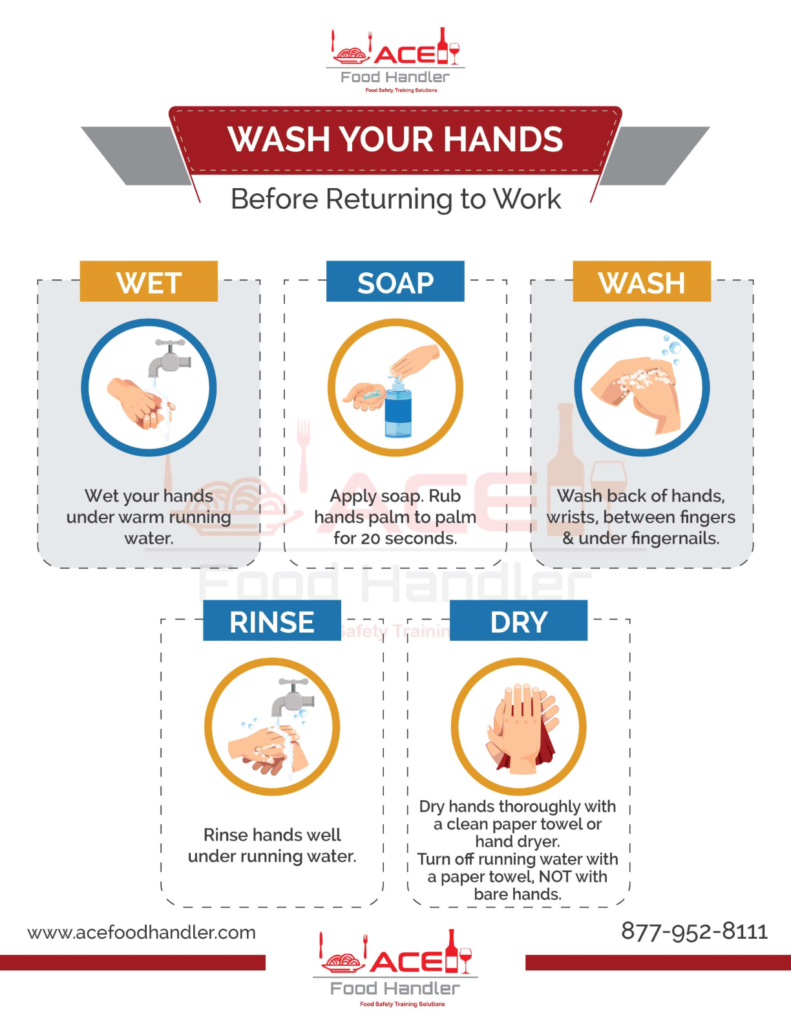
Proper Handwashing Techniques:
To achieve effective handwashing, the following step-by-step guide should be followed:
Wet hands thoroughly with warm water.
Apply enough soap to cover all surfaces of the hands.
Rub hands together vigorously, paying attention to cleaning all areas (front and back of hands, between fingers, and under nails) for at least 20 seconds.
Rinse hands thoroughly under running water, ensuring all soap residue is washed away.
Dry hands using a clean towel or air dryer, making sure to remove all moisture.
Key Practices for H2Safe Food Handling:
Proper handwashing should be integrated into various stages of food handling to ensure H2Safe practices:
Before handling food: Before initiating any food preparation tasks, it is essential to wash hands thoroughly. This step helps eliminate any potential contaminants present on the skin.
After handling raw foods: Raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs can contain harmful bacteria such as Salmonella or Campylobacter. Washing hands after handling these raw foods helps prevent cross-contamination with other ingredients or surfaces.
After using the restroom: Handwashing after using the restroom is crucial to eliminate potential pathogens and maintain personal hygiene.
Before and after wearing gloves: If gloves are used as a protective barrier during food handling, it is necessary to wash hands before wearing them to ensure cleanliness. Additionally, hands should be washed immediately after removing gloves to maintain hygiene.
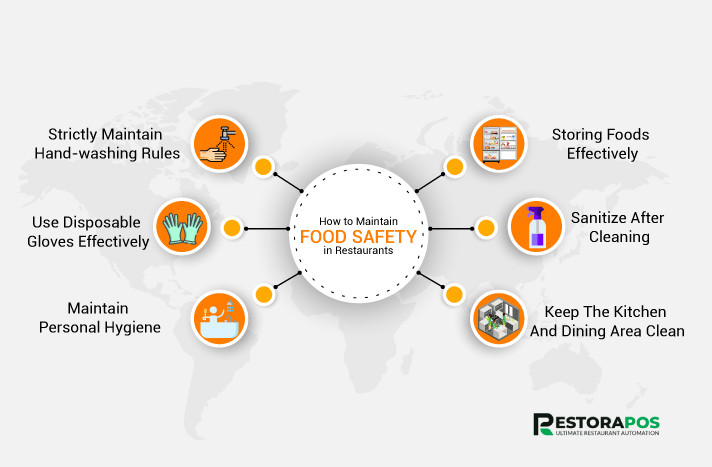
V. Additional Considerations for H2Safe Food Handling:
In addition to proper handwashing, several other factors contribute to overall food safety:
Clean and sanitized surfaces: Regularly cleaning and sanitizing food preparation surfaces, utensils, and equipment is essential to prevent the growth and spread of harmful bacteria.
Safe food storage: Storing food at appropriate temperatures is crucial for inhibiting bacterial growth. Refrigeration and proper temperature monitoring are vital to ensure food remains safe for consumption.
Proper food handling techniques: Avoiding cross-contamination by separating raw and cooked foods, using separate utensils and cutting boards, and cooking foods to recommended temperatures are all important aspects of safe food handling.
Conclusion:
Proper handwashing is a fundamental practice in H2Safe food handling. By understanding the science behind handwashing, following the recommended techniques, and integrating handwashing into various stages of food handling, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. However, handwashing alone is not sufficient. It should be complemented by other practices such as maintaining clean surfaces, safe food storage, and proper food handling techniques. By prioritizing food safety and adopting H2Safe practices, we can protect ourselves and others from the harmful effects of contaminated food. Let’s make handwashing a habit and ensure our meals are prepared with the utmost care and hygiene.