Food safety is a critical aspect of the food industry, impacting the health and well-being of consumers. It involves the proper handling, preparation, and storage of food to prevent foodborne illnesses. In this blog, we will explore the importance of food safety and the vital role that food safety guidelines play in ensuring the integrity of our food supply.
Importance of Food Safety
Food safety is of utmost importance for several reasons:
Protecting Public Health: Foodborne illnesses can have severe health consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. By implementing food safety practices, we can minimize the risk of contamination and safeguard the health of consumers.
Building Consumer Trust: Food safety is closely linked to consumer confidence. When individuals trust that the food they consume is safe, they are more likely to make informed choices and support businesses that prioritize food safety.
Legal Compliance: Compliance with food safety regulations is mandatory for food establishments. By adhering to these regulations, businesses can avoid legal consequences, including fines, penalties, and potential closure.
The Role of Food Safety Guidelines
Food safety guidelines provide a framework for food establishments to follow in order to maintain high standards of safety. These guidelines are based on scientific research, industry best practices, and regulatory requirements. Their key role is to assist food handlers and businesses in implementing effective food safety practices.
Understanding Foodborne Illnesses
Definition and Common Types
Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning, are caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. These illnesses can manifest in various forms, such as bacterial infections (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli), viral infections (e.g., norovirus, hepatitis A), parasitic infections (e.g., giardiasis), or toxins produced by bacteria (e.g., botulism).
Causes and Sources of Contamination
Food contamination can occur through various means, including:
Biological Contamination: Resulting from bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins produced by microorganisms.
Chemical Contamination: Arising from the presence of harmful substances like pesticides, cleaning agents, or food additives.
Physical Contamination: Involving foreign objects such as glass, metal, or plastic fragments.
Contamination can originate from sources such as improper handling, inadequate storage, unsanitary conditions, or contaminated raw ingredients.
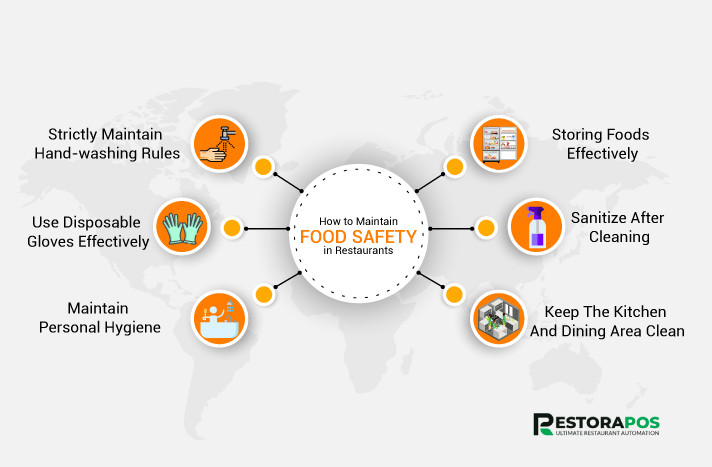
Food Safety Guidelines: Key Principles and Best Practices
Personal Hygiene
Handwashing: Thorough handwashing with soap and warm water is crucial before and after handling food, after using the restroom, touching animals, or handling chemicals.
Proper Attire and Personal Protective Equipment: Food handlers should wear clean uniforms, hair restraints, and appropriate protective gear to prevent cross-contamination.
Illness and Injury Reporting: Food establishments should have policies in place to ensure that staff members report any illnesses or injuries that may affect food safety, preventing the spread of infections.
Safe Food Handling and Preparation
Cross-contamination Prevention: Separate raw and cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination, use dedicated cutting boards and utensils, and practice proper storage techniques.
Proper Cooking Temperatures: Ensure that food is cooked to the recommended internal temperatures to kill harmful bacteria, using a food thermometer for accuracy.
Refrigeration and Storage Guidelines: Store perishable food items at proper temperatures, adhere to “first in, first out” (FIFO) practices, and regularly monitor and maintain refrigeration equipment.
Cleaning and Sanitization
Cleaning Procedures for Equipment and Surfaces: Establish regular cleaning routines for all food contact surfaces, utensils, and equipment, using appropriate cleaning agents and following manufacturer’s instructions.
Importance of Sanitizing: Implement sanitization protocols to eliminate bacteria and other microorganisms on surfaces, equipment, and utensils that come in contact with food.
Cleaning Schedule and Frequency: Develop a cleaning schedule based on the frequency of use, ensuring that all areas are regularly cleaned and sanitized.
Allergen Management
Identification and Labeling of Allergens: Clearly identify and label all ingredients that may cause allergies or intolerances, both in raw materials and prepared food items.
Preventing Cross-contact: Take precautions to prevent cross-contact between allergenic and non-allergenic ingredients during storage, preparation, and serving.
Proper Staff Training: Provide comprehensive training to staff members regarding allergen management, including awareness, prevention, and appropriate handling techniques.
Implementing Food Safety Guidelines in the Kitchen
AStaff Training and Education
Importance of Food Safety Training: Emphasize the significance of food safety training and ensure that all staff members receive adequate education on handling food safely.
Ongoing Education and Refreshers: Conduct regular training sessions and refresher courses to reinforce food safety practices and keep employees updated on new guidelines.
Certification Programs: Encourage employees to obtain food safety certifications, such as ServSafe, to enhance their knowledge and demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high standards.
BEstablishing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Developing Comprehensive SOPs: Create clear and detailed SOPs covering all aspects of food safety, including personal hygiene, food handling, cleaning, and allergen management.
Regular Review and Updates: Periodically review and update SOPs to incorporate changes in regulations, industry best practices, and lessons learned from internal and external audits.
Enforcing Compliance: Establish mechanisms to ensure that employees comply with the established SOPs, including regular monitoring, performance evaluations, and corrective actions.
Conducting Regular Inspections and Audits
Internal Self-Audits: Conduct routine internal audits to assess compliance with food safety guidelines, identify areas for improvement, and address any non-compliance issues promptly.
Third-party Inspections and Certifications: Engage third-party auditors or certification bodies to evaluate and validate the implementation of food safety practices in your establishment.
Addressing Identified Issues: Take immediate corrective actions to rectify any issues or deficiencies identified during inspections or audits, ensuring continuous improvement in food safety practices.
Regulations and Legal Considerations
Local and National Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations vary across jurisdictions, but they typically cover aspects such as proper food handling, storage, temperature control, labeling, and sanitation practices. Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations governing your region and ensure compliance to avoid legal consequences.
Legal Consequences of Non-compliance
Failure to comply with food safety regulations can result in severe legal consequences, including fines, penalties, loss of reputation, and even closure of the establishment. It is crucial to prioritize adherence to regulations and stay updated on any changes or additions to the existing laws.
The Role of Regulatory Agencies
Regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, play a vital role in overseeing and enforcing food safety regulations. These agencies conduct inspections, provide guidance, and take appropriate actions to protect public health and ensure compliance within the food industry.
Food Safety Culture
Importance of a Positive Food Safety Culture
Establishing a positive food safety culture within your organization is crucial for sustained success in maintaining high standards of food safety. A positive culture fosters a shared commitment to food safety practices, making it a core value for all employees.
Leadership and Communication
Leadership plays a crucial role in shaping the food safety culture of an organization. Managers and supervisors should lead by example, prioritize food safety, and communicate its importance to all staff members. Open and transparent communication channels should be established to facilitate the sharing of concerns, ideas, and best practices.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
Engaging and empowering employees is key to fostering a positive food safety culture. Involve employees in decision-making processes, encourage their feedback, and provide them with the necessary training and resources to fulfill their roles effectively. Recognize and reward employees who demonstrate exceptional commitment to food safety practices.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, prioritizing food safety is essential for the health and well-being of consumers and the success of food establishments. By understanding foodborne illnesses, implementing key food safety guidelines, training staff, and adhering to regulations, businesses can create a culture of safety and ensure the integrity of their food products. Continuous improvement, education, and a commitment to best practices are crucial for maintaining a robust food safety program. Let us strive together to make food safety a top priority and contribute to healthier communities.