Safe food handling practices are of paramount importance to ensure the well-being of individuals and prevent foodborne illnesses. One crucial aspect of safe food handling is preventing cross-contamination. In this blog, we will explore the concept of cross-contamination, its risks, and the significance of implementing effective prevention strategies. By understanding and implementing H2Safe practices, we can create a healthier and safer dining experience for everyone involved.
Understanding Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria or other microorganisms are transferred from one food item to another, leading to the contamination of previously safe food. This can happen through direct or indirect contact. Direct cross-contamination occurs when bacteria from raw food, such as raw meat or poultry, come into contact with cooked or ready-to-eat food. Indirect cross-contamination, on the other hand, happens when bacteria spread from contaminated surfaces, utensils, or hands.
Common sources of cross-contamination in the kitchen include cutting boards, knives, countertops, and even the hands of food handlers. It is crucial to identify these high-risk areas and surfaces to effectively prevent cross-contamination.
Importance of H2Safe Food Handling
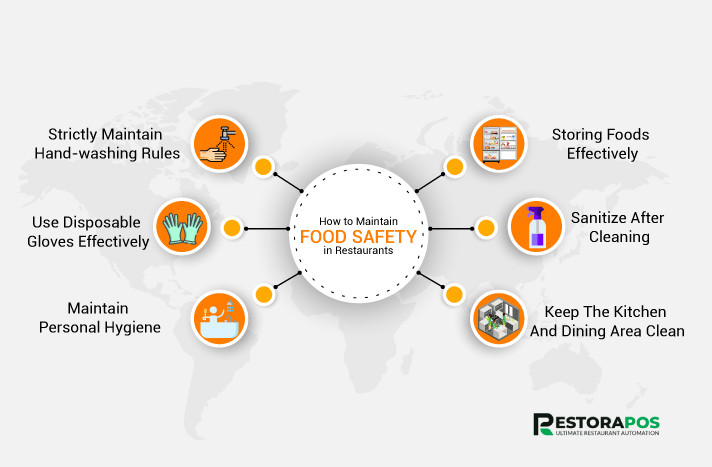
Proper hygiene plays a vital role in preventing cross-contamination. By following H2Safe practices, we can minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses and allergic reactions caused by cross-contamination. Foodborne illnesses can range from mild discomfort to severe complications, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
In addition to health risks, food establishments are subject to legal and regulatory requirements regarding food safety. Compliance with these regulations not only helps protect consumers but also safeguards the reputation and success of the business.
Identifying High-Risk Areas and Surfaces
To effectively prevent cross-contamination, it is essential to identify potential areas and surfaces that are prone to contamination. Kitchen equipment and utensils, such as cutting boards, knives, and countertops, can harbor bacteria if not properly cleaned and sanitized. Regular and thorough cleaning practices are necessary to maintain a safe food preparation environment.
Another critical aspect is ensuring proper personal hygiene. Hands can be a significant source of contamination if not washed frequently and adequately. Food handlers should follow strict handwashing practices to prevent the transfer of bacteria.
Additionally, storage and refrigeration practices should be carefully managed to prevent the cross-contamination of raw and cooked foods. Proper separation, labeling, and storage of different food items can significantly reduce the risk of contamination.
Implementing Effective Cross-Contamination Prevention Strategies
Implementing effective prevention strategies is key to maintaining a safe food handling environment. Establishing separate food preparation zones for raw and ready-to-eat foods can help minimize the risk of direct cross-contamination. Color-coded cutting boards and utensils can also be used to differentiate between food items and prevent cross-contamination.
Proper cleaning and sanitization of kitchen tools and surfaces are essential. Using appropriate cleaning agents and following recommended procedures will help eliminate bacteria and reduce the risk of indirect cross-contamination.
Handwashing is one of the most critical steps in preventing cross-contamination. Food handlers should wash their hands thoroughly and frequently, especially before and after handling different food items.
Furthermore, storage and handling practices should be followed diligently. Raw and cooked foods should be stored separately, and food items should be properly cooked to eliminate harmful bacteria.
Educating and Training Staff
Ensuring that all staff members are well-trained in safe food handling practices is crucial. Employers should provide comprehensive education on cross-contamination prevention, covering topics such as proper hygiene, cleaning and sanitization, and storage practices. Regular refresher courses and ongoing reinforcement of best practices should be implemented to maintain a high level of awareness and compliance among the staff.
Promoting Food Safety at Home
Extending the discussion beyond commercial kitchens, it is important to educate individuals on safe food handling practices in their own homes. By implementing similar H2Safe practices, consumers can protect themselves and their families from the risks of cross-contamination. Proper food storage, separation of raw and cooked foods, and regular cleaning and sanitization are essential in domestic kitchens as well.
Emphasizing the Role of Consumers
While food establishments and staff play a crucial role in preventing cross-contamination, consumers also have a responsibility in ensuring food safety. It is essential to educate customers about proper food handling and storage practices. By raising awareness and encouraging active participation in food safety practices, individuals can make informed decisions and contribute to a safer dining experience.
Conclusion:
Preventing cross-contamination is vital for safe food handling and the well-being of individuals. By understanding the concept of cross-contamination, identifying high-risk areas and surfaces, implementing effective prevention strategies, and educating both staff and consumers, we can create a healthier and safer dining experience. Prioritizing H2Safe practices in the kitchen and at home not only reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses but also fosters a culture of food safety that benefits everyone involved. Let us all commit to H2Safe food handling for a healthier future.